In 2006, Bursa Malaysia required issuers listed on the Main and ACE Markets to include disclosures of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities or practices in their annual reports. This mandate was perceived to focus mainly on the social dimensions of the business, including its employees and the community, and was considered to have a limited effect on value creation.
In recent years, there has been tremendous development and growth across the sustainability
ecosystem worldwide. The Sustainability Reporting ecosystem in Malaysia has also grown considerably in the past decade, from a largely nascent stage to one where all listed issuers are undertaking sustainability-related initiatives as well as producing Sustainability Statements or Reports on an annual basis.
A Sustainability Report usually begins with Materiality Assessment, which helps identify and understand the relative importance of specific ESG and sustainability topics to the organisation, the internal and external stakeholders. Exhibit 1 shows the Materiality Assessment process.
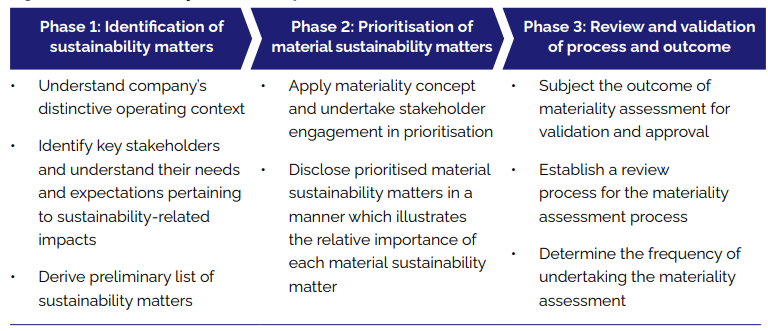
Exhibit 1. The Materiality Assessment Process, source: Bursa Malaysia
To conduct a Materiality Assessment in Bursa Malaysia Sustainability Reporting, companies start by identifying potential issues through both internal sources, such as business operations, strategic goals, risk assessments, and previous reports; and external sources, including industry trends, regulatory requirements, Sustainability Frameworks (e.g., Global Reporting Initiative, Sustainability Accounting Standard Board), and stakeholder expectations.
They engage stakeholders via surveys, interviews, focus groups, and consultations. Exhibit 2 shows how Maybank reveals the process with stakeholders including customers, investors, employees, communities, regulators and government.

Exhibit 2. Engaging with stakeholders, Maybank, source: Maybank Sustainability Report 2023
The significance of each issue is then assessed based on its potential impact on the business, including financial performance, operational efficiency, and stakeholder importance, using impact metrics such as financial implications, reputational risks, regulatory compliance, and social responsibility. Issues are prioritised by plotting them on a materiality matrix, with axes typically representing business impact and stakeholder concern. Exhibit 3 shows the materiality matrix of Tenaga Nasional Berhad in their 2022 Sustainability Report. The priority of the material matters will be the items closer to the top right corner (important to TNB’s business & TNB’s stakeholders)
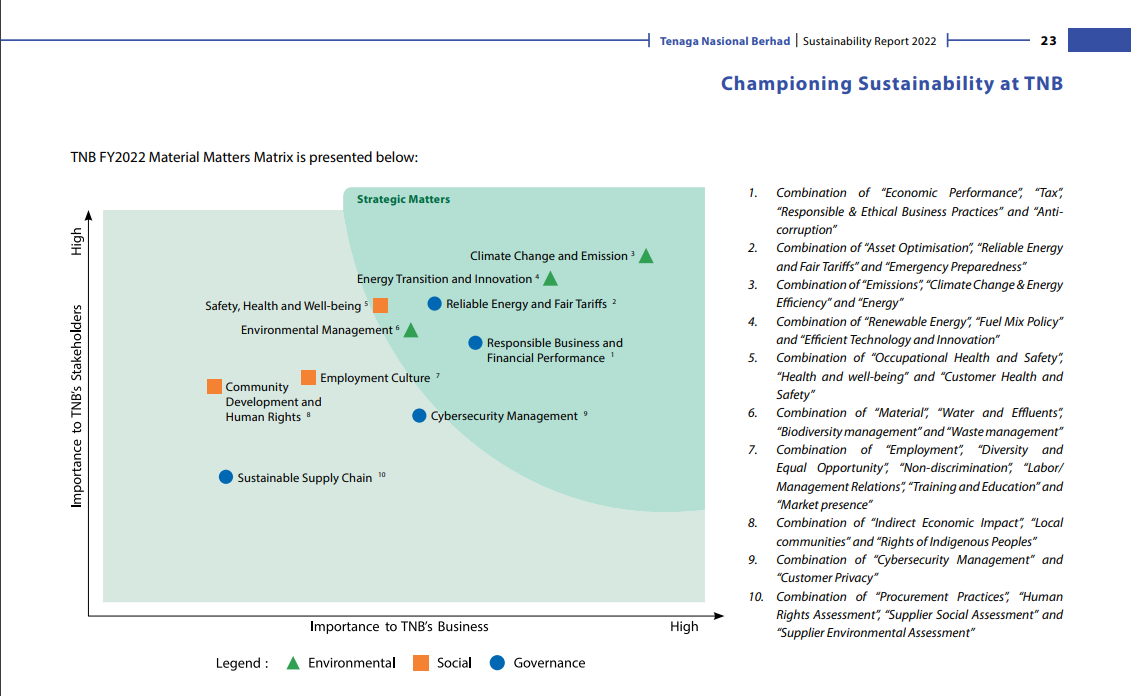
Exhibit 3. Materiality Matrix, source: Tenaga Nasional Berhad Sustainability Report 2022
Upon identifying the prioritised material matters, validation needs to be done. The process involves internal review by senior management and relevant departments, and external review with key stakeholders. The results, including the methodology and stakeholder engagement methods, are documented in the Sustainability Report, with strategies and actions developed to address the material issues and integrate them into business operations and strategic planning.
The report includes clear methodology, identifies and prioritises material issues, details on stakeholder involvement, impact analysis, and future outlook on managing and reporting these issues. The company should revisit and reconsider them from time-to-time, to ensure that recent developments and changes have been considered and incorporated.
Importance of Materiality Assessment
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures compliance with Bursa Malaysia’s Sustainability Reporting requirements.
- Enhanced Transparency: Demonstrates a company’s commitment to addressing key sustainability issues, building trust with stakeholders.
- Strategic Alignment: Helps align sustainability efforts with the company’s strategic goals, enhancing overall business performance.
- Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates potential risks related to Economics, Environment and Social (EES) issues, protecting the company’s reputation and financial stability.
Conclusion
Materiality assessment in Bursa Malaysia Sustainability Reporting is essential for identifying and prioritising the most significant ESG issues. It helps companies focus their sustainability efforts, ensuring that their reports are relevant, comprehensive, and aligned with stakeholder interests and regulatory requirements. By conducting thorough materiality assessments, companies can enhance their sustainability performance, manage risks, and create long-term value for both their business and stakeholders.